Cardiovascular Effects of Berberine: A Review of the Literature
- Ayurveda Interdisciplinary Research Minds Association, Mysore, India
- Department of Basic Principles, S. V Ayurvedic Medical College, Tirupathi, Andhra Pradesh, India
*Corresponding author: Executive Secretary and Researcher, Ayurveda Interdisciplinary Research Minds Association, #1179, 19th Main, 2nd stage, JP Nagar, Mysore 570008, Karnataka, India, Tel.: +91-99162-86955; E-mail: doctor.arvi@gmail.com
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14200/jrm.2017.6.0100
©2017, Aravind Bagade, MD
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND PHARMACOKINETICS
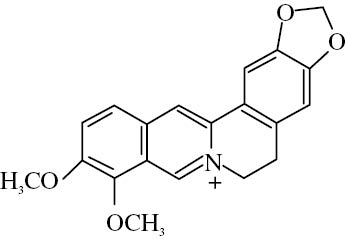
Figure 1:
Chemical structure of berberine.
VASCULAR ENDOTHELIUM AND THE HEART
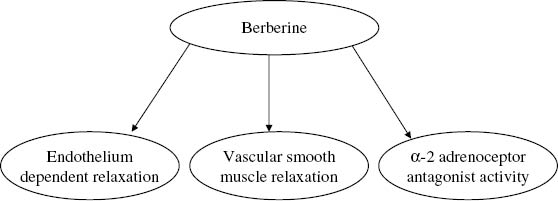
Figure 2:
Effects of berberine on endothelial homeostasis.
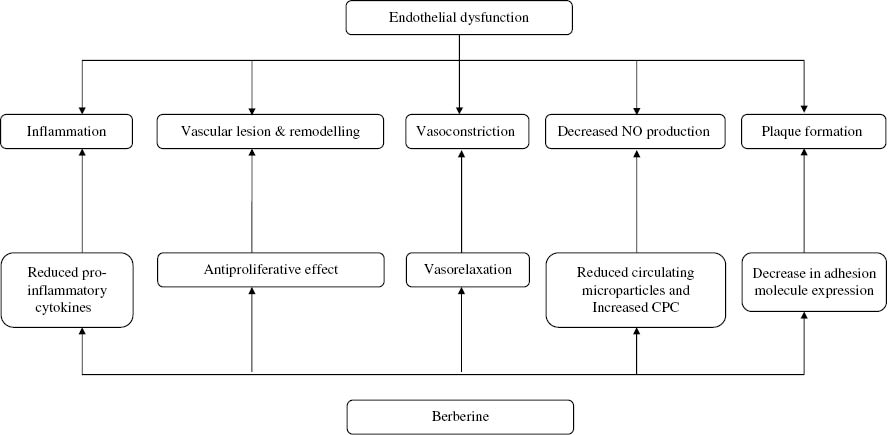
Figure 3:
Effects of berberine on endothelium and heart. (Reproduced from Affuso F, MercurioV, Fazio V, Fazio S. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of berberine. World J Cardiol. 2010;2:71—7, with permission.10)
BLOOD PRESSURE
GLUCOSE REGULATION
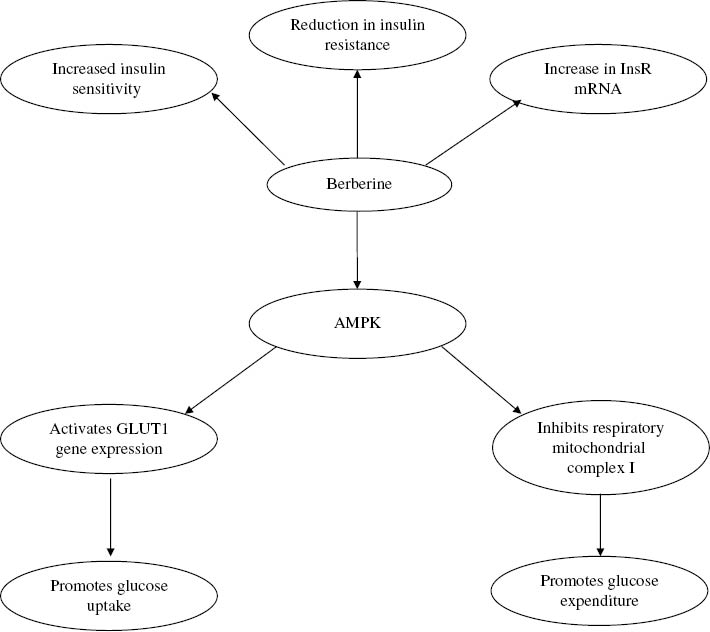
Figure 4:
Effects of berberine on glucose metabolism.
BLOOD LIPIDS
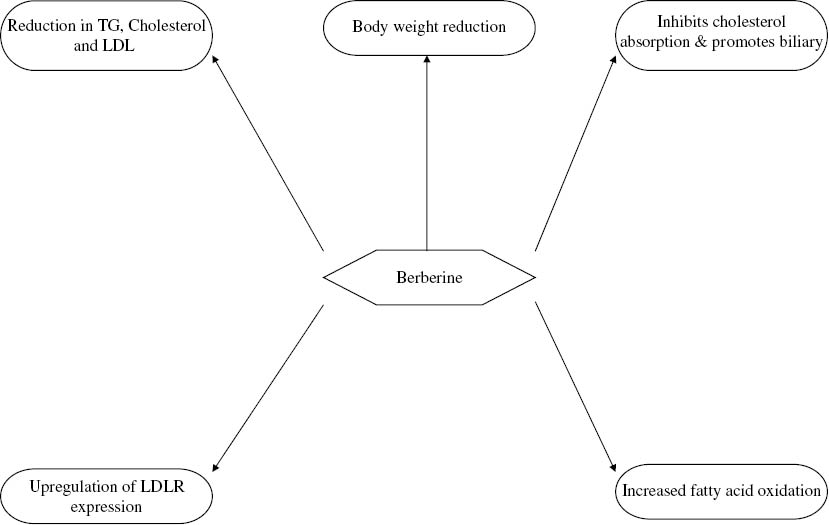
Figure 5:
Antihyperlipidemic actions of berberine.
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
INTERACTIONS, ADVERSE EFFECTS, AND SAFETY ISSUES
CONCLUSION
Figure 6:
Summary of the actions of berberine.
The authors wish to thank Elizabeth Sutherland, ND for her invaluable contribution to the development of this paper.
- Kamath S, Skeels M, Pai A. Significant differences in alkaloid content of Coptis chinensis (Huanglian), from its related American species.
- Gan RY. Bioactivities of berberine: an update.
- Kumar A, Ekavali, Chopra K, et al. Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: an update.
- Meneton P, Jeunemaitre X, de Wardener HE, MacGregor GA. Links between dietary salt intake, renal salt handling, blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Xia LM, Luo MH. Study progress of berberine for treating cardiovascular disease.
- Pan GY, Wang GJ, Liu XD, et al. The involvement of p-glycoprotein in berberine absorption.
- Feng R, Shou JW, Zhao ZX, et al. Transforming berberine into its intestine-absorbable form by the gut microbiota.
- Endemann DH, Schiffrin EL. Endothelial dysfunction.
- Rask-Madsen C, King GL. Mechanisms of disease: endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Affuso F, MercurioV, Fazio V, Fazio S. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of berberine.
- Zhang Y, Lee TS, Kolb EM, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase is involved in endothelial NO synthase activation in response to shear stress.
- Dagher Z, Ruderman N, Tornheim K, Ido Y. The effect of AMP-activated protein kinase and its activator AICAR on the metabolism of human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
- Ido Y, Carling D, Ruderman N. Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: inhibition by the AMP-activated protein kinase activation.
- Nagata D, Mogi M, Walsh K. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells is essential for angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress.
- Ouchi N, Shibata R, Walsh K. AMP-activated protein kinase signaling stimulates VEGF expression and angiogenesis in skeletal muscle.
- Hui KK, Yu JL, Chan WF, et al. Interaction of berberine with human platelet alpha 2 adrenoceptors.
- Henry PD, Cabello OA, Chen CH. Hypercholesterolemia and endothelial dysfunction.
- Montagnani M, Ravichandran LV, Chen H, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 are required for insulin-stimulated production of nitric oxide in endothelial cells.
- Affuso F, Ruvolo A, Micillo F, et al. Effects of a nutraceutical combination (berberine, red yeast rice and policosanols) on lipid levels and endothelial function randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
- Wang Y, Huang Y, Lam KS, et al. Berberine prevents hyperglycemia induced endothelial injury and enhances vasodilatation via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase and endothelial nitric oxide synthase.
- Zhang LS. Clinical usage of berberine.
- Ko WH, Yao XQ, Lau CW, et al. Vasorelaxant and antiproliferative effects of berberine.
- Zhao HP, Hong Y, Xie JD, et al. Effect of berberine on left ventricular remodeling in renovascular hypertensive rats [in Chinese].
- Wang J, Guo T, Peng QS, et al. Berberine via suppression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel improves vascular stiffness in mice.
- Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, et al. Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states.
- Kim SH, Shin EJ, Kim ED, et al. Berberine activates GLUT1-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
- Turner N, Li JY, Gosby A, et al. Berberine and its more biologically available derivative, dihydroberberine, inhibit mitochondrial respiratory complex I: a mechanism for the action of berberine to activate AMP-activated protein kinase and improve insulin action.
- Yin J, Gao Z, Liu D, et al. Berberine improves glucose metabolism through induction of glycolysis.
- Kong WJ, Zhang H, Song DQ, et al. Berberine reduces insulin resistance through protein kinase C-dependent up-regulation of insulin receptor expression.
- Zhang Y, Li X, Zou D, et al. Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine.
- Zhang H, Wei J, Xue R, et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression.
- Liu Y, Lou SY, He YM. Effects of berberine on cell proliferation, peroxisome proliferation activated receptor gamma, CAAT/enhancer binding protein mRNA and protein expression in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes [in Chinese].
- Zhou JY, Zhou SW, Zhang KB, et al. Chronic effects of berberine on blood, liver glucolipid metabolism and liver PPARs expression in diabetic hyperlipidemic rats.
- Huang C, Zhang Y, Gong Z, et al. Berberine inhibits 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation through the PPARgamma pathway.
- Kong W, Wei J, Abidi P, et al. Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins.
- Li H, Chen W, Zhou Y, et al. Identification of mRNA binding proteins that regulate the stability of LDL receptor mRNA through AU-rich elements.
- Wang Y, Yi X, Ghanam K, et al. Berberine decreases cholesterol levels in rats through multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of cholesterol absorption.
- Li XY, Zhao ZX, Huang M, et al. Effect of berberine on promoting the excretion of cholesterol in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic hamsters.
- Wang Y, Jia X, Ghanam K, et al. Berberine and plant stanols synergistically inhibit cholesterol absorption in hamsters.
- Cicero AF, Rovati LC, Setnikar I. Eulipidemic effects of berberine administered alone or in combination with other natural cholesterol-lowering agents: a single-blind clinical investigation.
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial.
- Zeng XH, Zeng XJ, Li YY. Efficacy and safety of berberine for congestive heart failure secondary to ischemic or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Marin-Neto JA, Maciel BC, Secches AL, et al. Cardiovascular effects of berberine in patients with severe congestive heart failure.
- Hong Y, Hui SS, Chan BT, Hou J. Effect of berberine on regression of pressure- overload induces cardiac hypertrophy in rats.
- Huang WM, Yan H, Jin JM, et al. Beneficial effects of berberine on hemodynamics during acute ischemic left ventricular failure in dogs.
- Imanshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of Berberis vulgaris and its active constituent, berberine.
- Chan E. Displacement of bilirubin from albumin by berberine.
- Tan YZ, Wu AC, Tan BY, et al. Study on the interactions of berberine displace other drug from their plasma proteins binding sites.
- Wang YS.
- Zilaee M, Kermany T, Tavalaee S, et al. Barberry treatment reduces serum anti-heat shock protein 27 and 60 antibody titers and high- sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with metabolic syndrome: a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial.
- Yarnell E. Recent clinical advances with berberine.